

Helium (He) is a colorless, odourless, tasteless, non-toxic, inert and monatomic gas. It is the lightest noble gas with the lowest boiling point among all the elements.
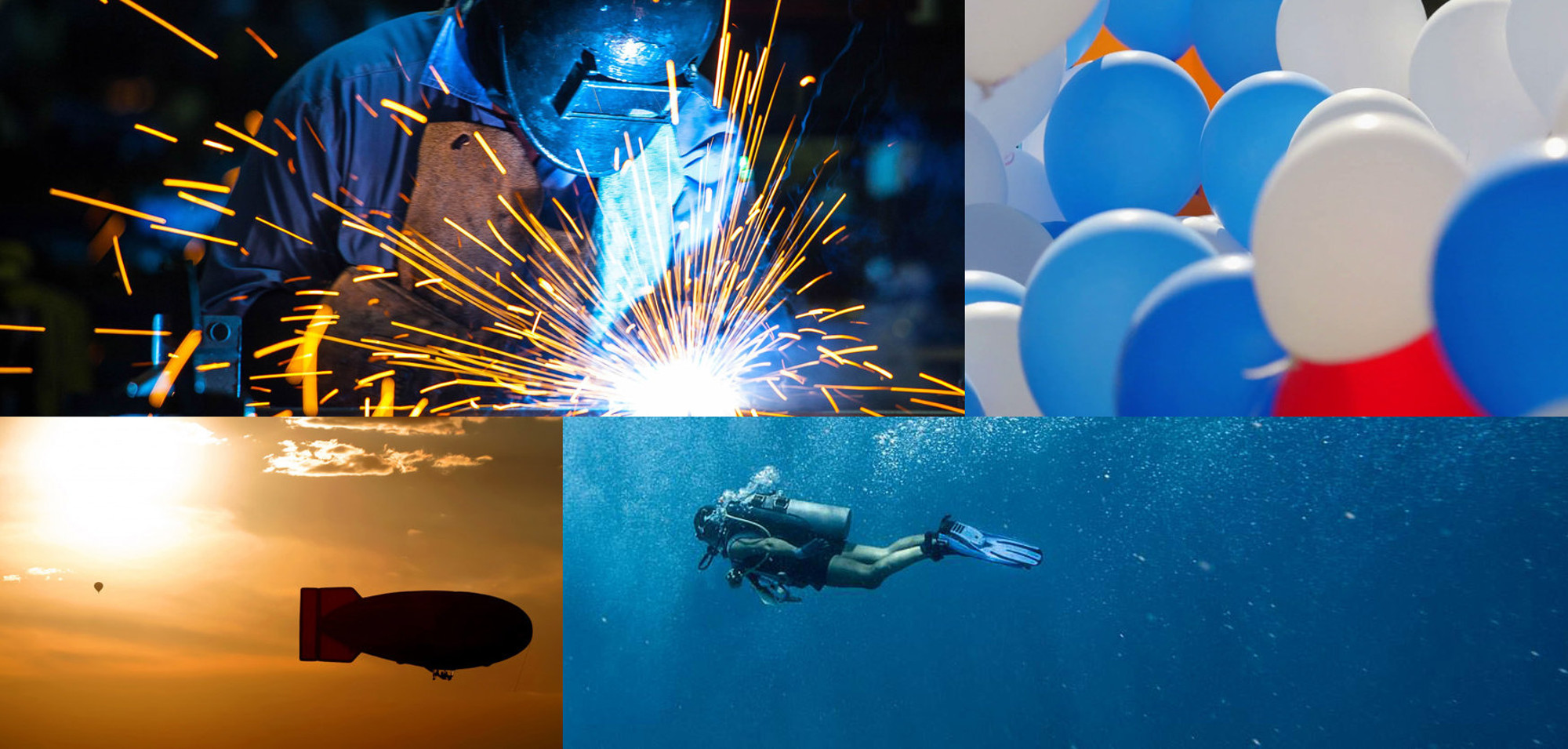
In daily life, Helium might be commonly known as a gas that fills decorative balloons, weather balloons and airships. In professional and industrial field, Helium is also widely used. Namely; as an inert shield for arc welding, to create an artificial atmosphere for deep-sea divers and even to scan barcodes in modern market checkouts.
Rarely known for public, Helium holds important roles in the operations of many high-technology tools and machineries such as MRI Scanners, NMR Spectrometers, Satellite instruments and the making of fibre optics and semiconductors.
The new inventions that involves the usage of Helium is also increasing from time to time. Hence, the future expects to find Helium usage to be wider than it is already now.
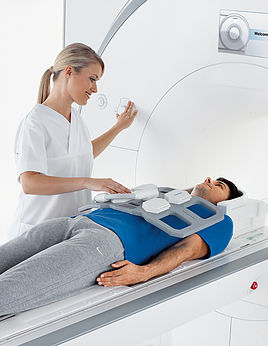
As a noble gas with the lowest boiling point, Helium is suitable to be the super-coolant for Cryogenic applications such as MRI Scanners, NMR Spectroscopy to Superconducting Magnetic Energy Storage.

Because it is unreactive, Helium is chosen to provide an inert protective atmosphere in the making of fiber optics and semicondutors.
Due to its light and non-reactive characteristics, Helium is preferred as a lift gas to fill balloons, blimps, scientific balloon and airships.

Helium is used in various other functions such as rockets cleaning, rocks and other minerals age estimation, solar telescopes heating prevention and many more. The prospects of Helium usage keeps on expanding following the advancement of technology.